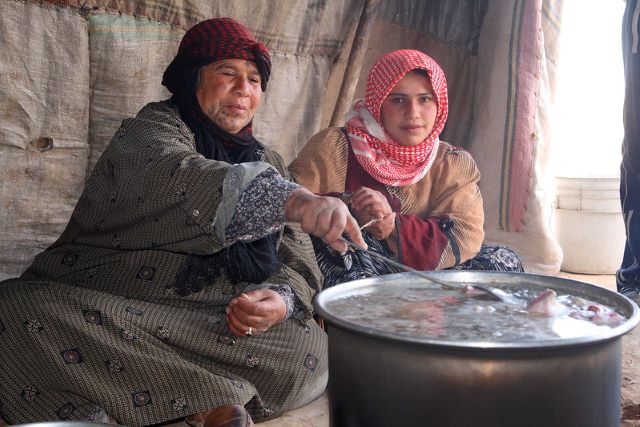
 In Africa, nearly 90% of women use open fire cooking methods. The same is common for women in developing countries throughout the world. This system can often take hours to cook a full meal. The insulated Wonderbag, a heat retention cooking device, aims to change lives and create a sustainable life for those living in poverty, especially women.
In Africa, nearly 90% of women use open fire cooking methods. The same is common for women in developing countries throughout the world. This system can often take hours to cook a full meal. The insulated Wonderbag, a heat retention cooking device, aims to change lives and create a sustainable life for those living in poverty, especially women.
The Insulated Wonderbag
In developing countries, gendered roles like cooking and tending to the household take up a lot of time. The amount of time spent cooking could be better used on activities that result in the progression of women, such as education and development. Often, women are disproportionately responsible for cooking meals and the labor that goes into the open fires that are required for such cooking. A South African entrepreneur decided to design an invention to help address these difficulties. The insulated Wonderbag is an eco-technology innovation that saves girls and women hours of time and labor and improves indoor air quality and overall health, among other benefits.
How the Wonderbag Began
The idea behind this invention comes from Sarah Collins, a local South African innovator with extensive knowledge of social development and a love for the environment. Collins grew up watching the women before her use cooking tricks to keep food warm when the power went out. One of these tricks, used by her grandmother, was letting hot pans of food sit in cushioned pads to remain warm. A life-changing yet straightforward concept that Collins took and made her own.
The Simple Magic of the Wonderbag
First and foremost, the Wonderbag is a product meant to alleviate women and girls’ daily struggles as caregivers and enable them to pursue education and employment. The Wonderbag works without electricity or gas and is made of upcycled materials such as poly-cotton and chipped-foam. Essentially, it functions similarly to a crockpot or a slow cooker. The insulated Wonderbag allows food, once brought to the boil by traditional cooking methods, to continue cooking for up to 12 hours inside the Wonderbag.
The Benefits of the Wonderbag
- Females regain four to six hours of their day
- Boosts household incomes up to $2 a day
- Saves more than 1300 hours for girls and women each year, enabling them to go to school, learn skills and find employment
- Raises incomes of women living in poverty
- Decreases the use of fossil fuels for cooking by 70% and thus also the associated negative health impact
- Allows women to re-invest their earnings into providing healthier meals for their families
The Impacts of the Wonderbag
Since 2008, the revolutionary Wonderbag has been distributed around the world. Thus far, it has had an impressive impact. The introduction of the Wonderbag into communities allows women the chance to build their own businesses and create jobs for others. These businesses range from serving warm meals to sewing new bags. Moreover, every time a Wonderbag is bought, another is donated to women in need in Africa, continuing the cycle of prosperity.
More than 130 NGOs in Kwazulu Natal, South Africa, benefitted from reselling Wonderbags to generate an income, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Collectively, these NGOs generated almost two million South African rands to sustain their operations.
Overall, the global need for the insulated Wonderbag continues to grow. So far, there are more than one million Wonderbags worldwide. With every purchase, $1 goes toward subsidizing bags for people in vulnerable communities. The Wonderbag is an innovative solution to combat global poverty.
– Sallie Blackmon
Photo: Flickr
 With its formal recognition as a country in 2011, South Sudan stands as the youngest country on Earth. With a population of more than 10 million people, all eyes are focused on how the country will develop. Born out of civil war and gruesome conflict, the first nine years of South Sudan’s existence have presented numerous humanitarian issues. Widespread hunger, unsanitized water, crumbling infrastructure and underfunded education plague the youngest country in the world. If the new nation wants to grow into a fruitful nation, it must address the widespread poverty and the issues that come along with it.
With its formal recognition as a country in 2011, South Sudan stands as the youngest country on Earth. With a population of more than 10 million people, all eyes are focused on how the country will develop. Born out of civil war and gruesome conflict, the first nine years of South Sudan’s existence have presented numerous humanitarian issues. Widespread hunger, unsanitized water, crumbling infrastructure and underfunded education plague the youngest country in the world. If the new nation wants to grow into a fruitful nation, it must address the widespread poverty and the issues that come along with it. A whole
A whole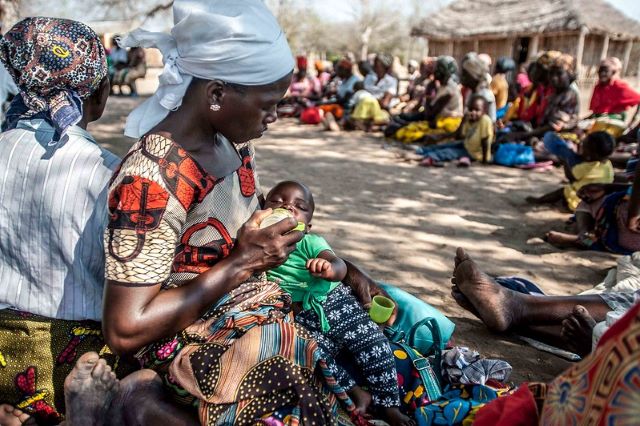  The provision of foreign aid from the United States serves as a multifaceted solution and preventative measure to many issues that ultimately impact the United States. In assisting with the development of under-resourced countries and those afflicted by natural disasters and conflict, the country’s interest in strengthening U.S. eminence in the global political ecosystem is served, as is the initiative to foster and stabilize democracies that are essential in maintaining global peace. Mozambique is one such country that receives aid from the United States. Nearly half of the population lives in poverty and while having managed to combat that statistic with an
The provision of foreign aid from the United States serves as a multifaceted solution and preventative measure to many issues that ultimately impact the United States. In assisting with the development of under-resourced countries and those afflicted by natural disasters and conflict, the country’s interest in strengthening U.S. eminence in the global political ecosystem is served, as is the initiative to foster and stabilize democracies that are essential in maintaining global peace. Mozambique is one such country that receives aid from the United States. Nearly half of the population lives in poverty and while having managed to combat that statistic with an 
 Children are the world’s future but
Children are the world’s future but  The agricultural sector is a critical facet of Sub-Saharan Africa’s (SSA) economy. As of 2015, women make up around 40% of the SSA’s agricultural labor force. Although their contribution is critical, due to discriminatory laws and social norms, a large gender gap within this sector continues to persist. However, many have come to realize the potential that lies behind empowering and educating female agriculture workers in Africa. By decreasing the gender gap and expanding females’ access to land and resources, these women have the potential to
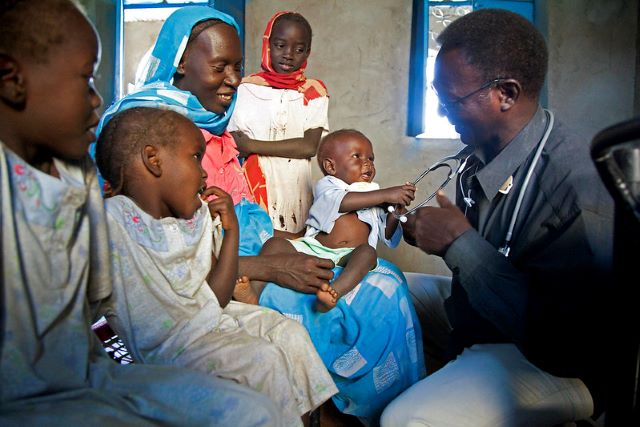
The agricultural sector is a critical facet of Sub-Saharan Africa’s (SSA) economy. As of 2015, women make up around 40% of the SSA’s agricultural labor force. Although their contribution is critical, due to discriminatory laws and social norms, a large gender gap within this sector continues to persist. However, many have come to realize the potential that lies behind empowering and educating female agriculture workers in Africa. By decreasing the gender gap and expanding females’ access to land and resources, these women have the potential to 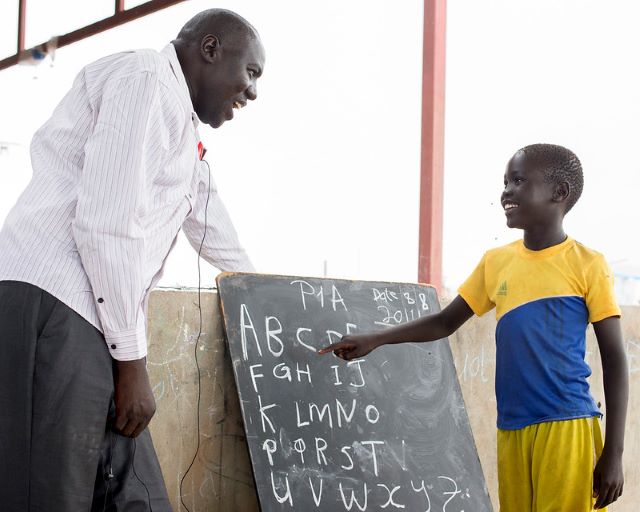 Over three million children in Sudan do not attend school. The severe gap in the education system continues the cycle of poverty in the country. Chronic underdevelopment and conflict are two of the most significant reasons children in Sudan are out of school. Girls face additional hurdles such as cultural pressures and traditional views that prevent them from receiving an education. While 76% of primary age children attend school, in secondary, the number
Over three million children in Sudan do not attend school. The severe gap in the education system continues the cycle of poverty in the country. Chronic underdevelopment and conflict are two of the most significant reasons children in Sudan are out of school. Girls face additional hurdles such as cultural pressures and traditional views that prevent them from receiving an education. While 76% of primary age children attend school, in secondary, the number  Despite having some of the greatest potential for development in Africa and a vast amount of resources, Nigeria remains
Despite having some of the greatest potential for development in Africa and a vast amount of resources, Nigeria remains  Education has long been proven as a tool for poverty reduction. In fact, UNESCO estimates that if all people in low-income countries had basic reading skills, an estimated
Education has long been proven as a tool for poverty reduction. In fact, UNESCO estimates that if all people in low-income countries had basic reading skills, an estimated 