At the start of 2024, roughly two-thirds of Zambia’s population lacked reliable access to the internet, highlighting a critical barrier to national development. In light of this issue, Hakainde Hichilema, the president of Zambia, has established ambitious goals to connect his nation to the internet and bring Zambia into the digital age. President Hichilema and his government aim for 80% digital inclusion in Zambia by 2026.
At the start of 2024, roughly two-thirds of Zambia’s population lacked reliable access to the internet, highlighting a critical barrier to national development. In light of this issue, Hakainde Hichilema, the president of Zambia, has established ambitious goals to connect his nation to the internet and bring Zambia into the digital age. President Hichilema and his government aim for 80% digital inclusion in Zambia by 2026.
What is Digital Inclusion?
Digital inclusion encompasses more than just internet access. It integrates digital literacy training to navigate the internet, high-quality tech support and access to applications that maximize the utility of internet access. Digital inclusion also incorporates measures that combat poverty. For example, easier access to job opportunities that someone without internet access might not discover. President Hichilema has diligently worked to tackle poverty in Zambia by enhancing digital connectivity through a variety of measures.
Hakainde Hichilema and Key Government Initiatives
Hakainde Hichilema has been the leader of Zambia’s United Party for National Development since 2006. He grew up in a rural community in the Monze District of Zambia, a region that he is now helping gain widespread access to reliable internet. His presidency is committed to pioneering how Zambia’s government can fight poverty by improving digital connectivity.
While running for president, he focused on education, jobs and digital inclusion in Zambia. His plan to improve digital inclusion in Zambia includes tax incentives, improvements to digital infrastructure, partnerships with companies for access to satellites, foreign partnerships with wealthier nations and building a free wi-fi network that all Zambians, including the poor, can take advantage of.
The details of these initiatives are as follows:
- Taxes. President Hichilema has instituted tax waivers on ICT equipment to spur private sector investment. This has yielded $54 million in investment. As companies invest capital in the country, it stimulates the economy. In the long term, it fosters a tax base that can subsequently fund various social programs that address poverty and assist those most in need.
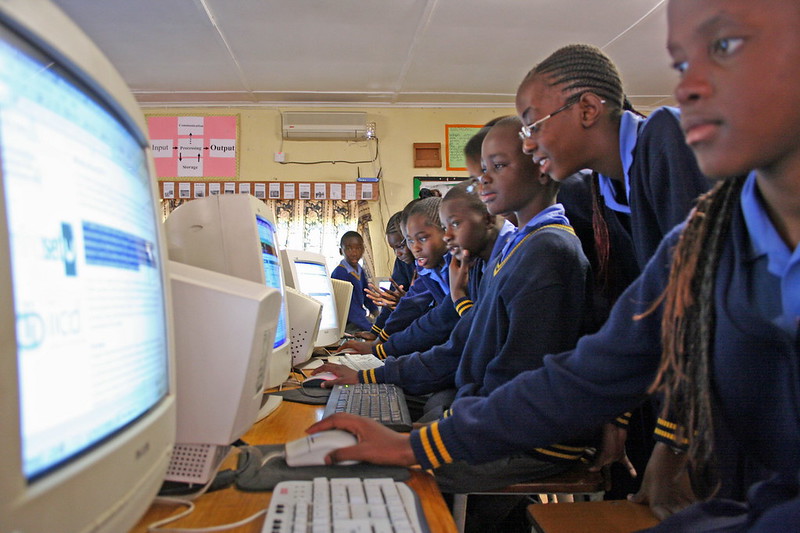
- Infrastructure. Zambia’s government plans to link itself to all eight of its neighboring countries via high-capacity optic fiber cables. This is in addition to the 379 communication towers Zambia plans to erect, primarily in rural areas. Zambia has also launched a 5G network through collaboration with MTN and Huawei. These measures will greatly improve Zambia’s Wi-Fi network infrastructure, linking every citizen nationwide to the internet and enabling them to obtain information that was once inaccessible.
- Satellites. Zambia has collaborated with Starlink to deliver affordable internet services to underserved communities. Through this collaboration, many rural communities now access the internet at public libraries, schools and hospitals. Starlink’s satellites provide internet access to hospitals, empowering them to acquire up-to-date information regarding medications or new health guidelines. Doctors can communicate with patients via online communication platforms. This allows them to support their patients should any issues arise after visits. This system closely mirrors practices in the United States (U.S.), where a doctor remains accessible weeks after a visit if issues emerge.
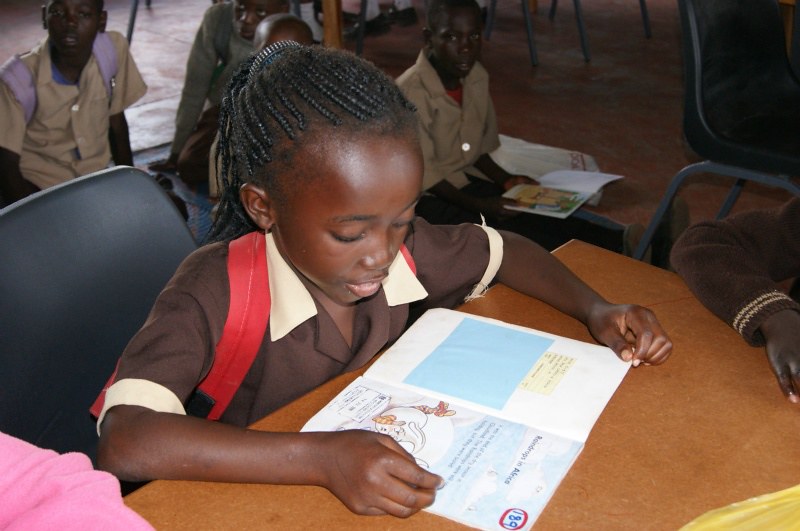
- National Free Wi-Fi. ZamFree is an initiative to extend free Wi-Fi to Zambians in key public spaces, including markets, schools, airports and hospitals. Liquid Telecom, another organization working to broaden Wi-Fi access in Zambia, champions Hichilema’s plan to link 1,291 secondary schools to the internet. Free Wi-Fi narrows the divide between the rich and the poor. Individuals experiencing poverty can leverage the internet to participate in job training programs or enroll in school. As their skillset grows, they can secure employment and address workforce gaps more easily.
- International Partnerships. The African Development Bank has considered establishing its headquarters in Zambia. This would not only generate jobs but also transform Zambia into a major hub for expanding internet access across much of Africa. President Hichilema has also initiated collaboration with the Czech Republic. The aim is to establish scholarships for professionals specializing in IT, AI and cybersecurity. These partnerships strengthen Zambia’s relationship with countries worldwide, enhancing diplomacy.
Ending Poverty with the Use of Digital Tools
Improvements to internet infrastructure in Zambia carry the potential to fight poverty by improving digital connectivity and empowering more people to utilize the internet. Indeed, doctors in hospitals can leverage the internet to reach patients, extending health care access to those facing unreliable transportation or mobility issues. Teachers can engage students across all levels of education, from pre-K through college. Overall, these examples, among many others, highlight the potential to fight poverty through improved digital inclusion in Zambia.
– Jeff Mathwig
Jeff is based in Philadelphia, PA, USA and focuses on Global Health and Politics for The Borgen Project.
Photo: Flickr
 Rivers are critical to the
Rivers are critical to the 
 Lobito is a municipality in
Lobito is a municipality in