2 Diseases Impacting Afghanistan
 Since the early 2000s, Afghanistan’s disease prevention and treatment services were far below sustainable, with only 11 physicians and 18 nurses per 100,000 civilians working in 2003. As foreign aid began to pour in, these numbers slowly improved. However, infant, child and maternal mortality rates remain the highest globally, alongside many other diseases impacting Afghanistan today. Currently, two diseases impacting Afghanistan include tuberculosis and polio, which the Western world is well equipped to diagnose with far less difficulty.
Since the early 2000s, Afghanistan’s disease prevention and treatment services were far below sustainable, with only 11 physicians and 18 nurses per 100,000 civilians working in 2003. As foreign aid began to pour in, these numbers slowly improved. However, infant, child and maternal mortality rates remain the highest globally, alongside many other diseases impacting Afghanistan today. Currently, two diseases impacting Afghanistan include tuberculosis and polio, which the Western world is well equipped to diagnose with far less difficulty.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a highly infectious, airborne disease impacting many Afghan people. Tuberculosis symptoms include a dry cough (sometimes with blood), fatigue, loss of appetite, night sweats and others. Yet, early diagnosis and quality treatment are easily accessible in the United States, preventing mass outbreaks.
The World Health Organization states that tuberculosis kills around 13,000 Afghans yearly, making it a disease that impacts Afghanistan severely. In 2014, Afghanistan had approximately 58,000 new tuberculosis cases. Only 56% of these cases were diagnosed and provided with adequate treatment. Keeping the disease at bay only becomes more challenging with up to 25,000 Afghan people left undiagnosed and untreated.
However, with WHO’s help, BRAC Afghanistan and USAID started a community-based TB DOTS program to control tuberculosis outbreaks. Through the program, diagnostic facilities for tuberculosis expanded and existing facilities were further equipped with microscopy screening technology. After the initiation of these health programs, more Afghans saw doctors and received treatment for tuberculosis: Since the program’s launch in 2004, access to dots has expanded from 15 to 121 clinics two years later. By 2006, more than 6,000 community health workers had trained under the program, of which 53 percent of trainees were women. Through the continued funding and advancement of the TB DOTS program, tuberculosis may slowly begin to lose its footing and become a lower-risk illness.
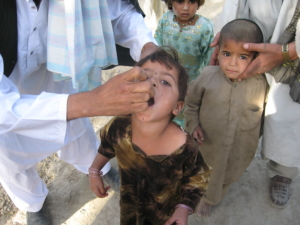
Poliomyelitis (Polio)
Polio is a viral illness that can lead to severe nerve damage and injury, eventually leading to paralysis and sometimes death. Afghanistan, Nigeria and Pakistan remain the only countries worldwide that have yet to eradicate polio. Due to inconsistent vaccination rates at birth, polio remains a disease impacting Afghanistan heavily today. In the 2015 report by the polio eradication initiative, researchers found that reported polio cases in Afghanistan had decreased since years prior. However, Afghanistan is still far from eradication.
In efforts to eradicate the polio virus worldwide, UNICEF worked with WHO to find innovative ways to give every child polio vaccines. The program implemented three National Immunization Days (NIDs) to increase access to polio vaccines and potential treatment if necessary. NIDs aim to reach nearly 10 million children through house-to-house and health facility-based approaches.
Furthermore, in collaboration with UNICEF and WHO, Afghanistan’s Ministry of Health is investing in a polio program to support vaccinators, community mobilizers, influencers, volunteers and campaign coordinators to reach children in need of vaccines. According to UNICEF, 392,000 polio branded items were distributed in 2020 to Afghan students to raise awareness about the disease’s severity, prevention and symptoms. As efforts continue, polio may become a disease impacting Afghanistan far less than before.
Why it Matters
Though efforts to improve health care access and treatments in Afghanistan have increased, much work still needs to be done. Today, tuberculosis is a disease that the U.S. quickly diagnoses and treats, while, in Afghanistan, the disease is often more threatening.
Afghanistan’s Ministry of Public Health and emergency operating system know how to help their people lead healthier lives yet lack the resources to do so. In funding programs that help international organizations and ministries provide the support needed for their people, both tuberculosis and polio can become low-priority diseases for all.
– Opal Vitharana
Photo: Flickr
