Ending Poverty Through Mobile Banking
With populations in the developing world on the steady rise and technology becoming more user-friendly, there is no doubt that technology will make drastic changes to the developing world in the next decade.
In a recent 2015 Gates Annual Letter published by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Gates declared that innovation will play a vital role in improving the lives of people in poor countries in the next 15 years.
Moreover, Melinda Gates argues that an increase in access to mobile banking through cell phones will provide impoverished people with the opportunity to save what they earn or perhaps borrow what they need at a low rate.
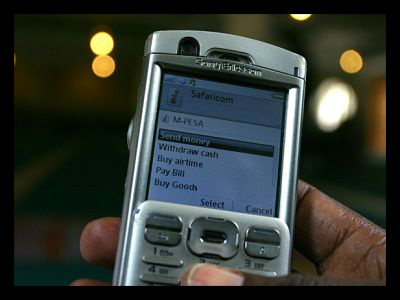
One of the many benefits of mobile banking is its socio-economic impact. The country of Kenya was known to have an underdeveloped banking infrastructure, high poverty rate and a large population of migrant people. Since the introduction of mobile banking in Kenya, financial inclusion is reported to have increased to 80 percent. Along with significant changes and improvements in global health and agricultural production, increased access to mobile technologies in developing nations is the starting point to something greater.
Developing countries are limited by the physical infrastructure of financial institutions, which means that a large part of their population is not included in a banking system. Financial inclusions have an important impact on the lives of people. Reports indicate that when poor people receive access to financial services, their cash management improves and creates better infrastructure for business and development of markets.
This change in the infrastructure in developing nations is a start to change the way people live in these countries. A small technological innovation like the mobile phone has made huge impacts in providing the opportunity to build a more developed economy in these countries.
Other innovations in technology have become popular in benefiting the developing world as well. Telecenters are an example of how technology has changed in order to suit those living in remote areas. Telecenters range from innovations in the education sector to the medical industry.
For learning, distance education developed by technology has the ability to make every child a scholar. For health, telemedicine has the ability to change dysfunctional rural health-care systems by providing clinical health care at a distance.
Other small inventions, such as the Soccket and Lifestraw, have been developed to help those living in poverty-stricken areas and to improve the lives of those individuals.
This shows how a simple change in technology can change the lives of people living in poverty. These types of actions should be embedded in all development efforts that aim to challenge poverty through innovations of new technology.
Although technology does not end poverty, it allows people to create connections and relationships that together can break down the systems that keep people poor, and then it is up to humanity to end it.
– Sandy Phan
Sources: Bill Gates’ Blog, Consultive Group to Assist the Poor
